- Call Us: 7440777771
- |
- Mail: operation.eye@sbhhospital.com
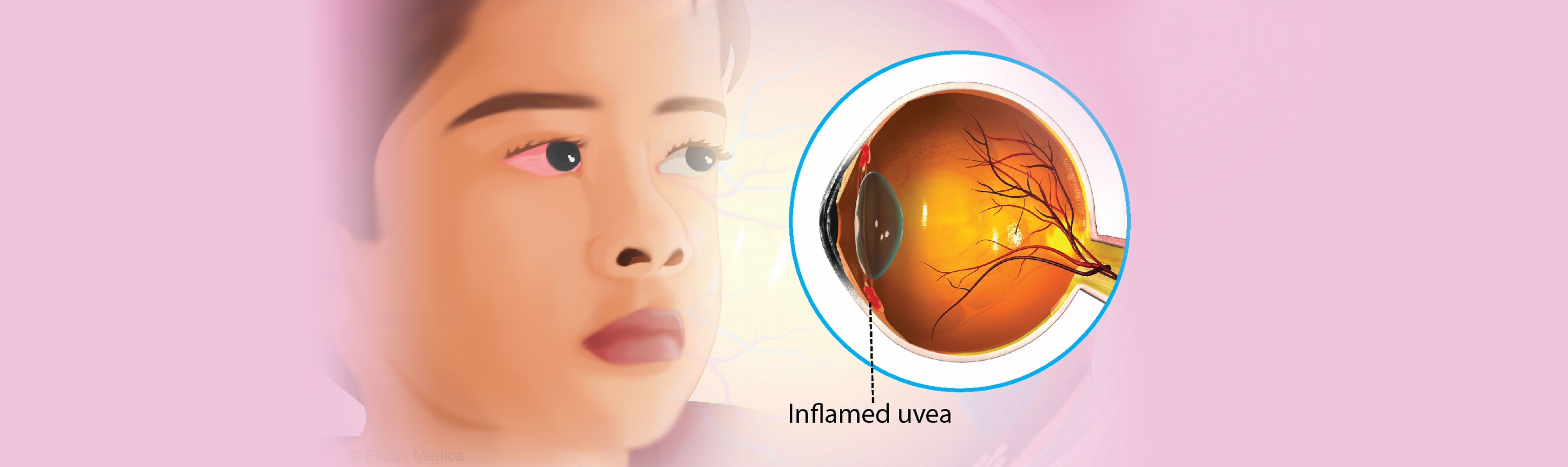
The uvea is a part of the eye with three main structures: the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. It is located between the sclera and the retina and is crucial in maintaining the eye's health and function. The iris is the coloured part of the eye, and it controls the amount of light that SBHServices enters the eye by adjusting pupil size. The ciliary body produces the aqueous humor, which nourishes the cornea and lens, while the choroid supplies oxygen and nutrients to the outer layers of the retina.
Uveitis is a condition that affects the uvea and can lead to inflammation, pain, and vision loss if left untreated. Infections, autoimmune disorders, or trauma can cause it. The uvea also plays a role in some eye diseases, such as glaucoma and age-related macular degeneration, which can affect the choroid and lead to vision loss. Regular eye exams at SBH can help detect and prevent such conditions, and timely treatment can help preserve vision.
Autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus can cause inflammation in the uvea, leading to uveitis. Infections such as herpes simplex virus and toxoplasmosis can also affect the uvea and cause inflammation. Trauma to the eye can cause uveitis as well.
Uveitis can cause various symptoms, including eye pain, redness, and sensitivity to light. Treatment may involve anti-inflammatory medications such as corticosteroids, antibiotics, or antiviral medications if an infection occurs.